I like to keep the stuff simple and understand them at least to hold 5 min talk about any issue...
So i would like to summarize a few thing in 10000 fit level.
If anybody would like to go deeper and dig for more information, i am more then 100% sure he/she will know where to look.
So, my first summary will be related to PON Technology:
PON (Passive Optical Network) it is basically telling us about connectivity of the central office and end user by optical network ( by fiber). why Passive? Because we don't need other equipment on the way, no amplifiers and bridges to keep the signal reaching the destination.
So in the office we have an equipment names: OLT (Optical Line Terminal) which is aggregating the lines from the ONT (Optical Network Terminal) which is sitting in the end user premises.
This topology calls FTTx.
x- means different types of environment for example:
So i would like to summarize a few thing in 10000 fit level.
If anybody would like to go deeper and dig for more information, i am more then 100% sure he/she will know where to look.
So, my first summary will be related to PON Technology:
PON (Passive Optical Network) it is basically telling us about connectivity of the central office and end user by optical network ( by fiber). why Passive? Because we don't need other equipment on the way, no amplifiers and bridges to keep the signal reaching the destination.
So in the office we have an equipment names: OLT (Optical Line Terminal) which is aggregating the lines from the ONT (Optical Network Terminal) which is sitting in the end user premises.
This topology calls FTTx.
x- means different types of environment for example:
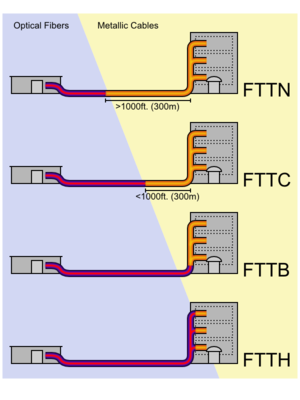
· FTTN - Fiber-to-the-node - fiber is terminated in a street cabinet up to several kilometers away from the customer premises, with the final connection being copper.
· FTTC - Fiber-to-the-curb - this is very similar to FTTN, but the street cabinet is closer to the user's premises; typically within 300m.
· FTTB - Fiber-to-the-building or Fiber-to-the-basement - fiber reaches the boundary of the building, such as the basement in a multi-dwelling unit, with the final connection to the individual living space being made via alternative means.
· FTTH - Fiber-to-the-home - fiber reaches the boundary of the living space, such as a box on the outside wall of a home.
· FTTP - Fiber-to-the premises - this term is used in several contexts: as a blanket term for both FTTH and FTTB, or where the fiber network includes both homes and small businesses.
· FTTD - Fiber-to-the-desk - fiber connection is installed from the main computer room to a terminal or fiber media converter near the users desk.
OK, then over mentioned above typologies we have different type of technologies which is helping us to send the information over the PON infrastructure:
1) APON/BPON - ATM PON/Broadband PON:
Very old and not fit to the today requirements of the networks demands. Slow as well comparing the the other.
2) EPON - Ethernet PON
Uplink shared, downlink not.
3) GPON - Gigabyte capable PON
Name talking for it self.
Uplink shared, downlink not.
3) GPON - Gigabyte capable PON
Name talking for it self.
Summary:
4) WDN PON
One reserve channel for each end user
U: 1-10Gbps, D: 1-10Gbps, Distance: 20km, Users per line 100.
That’s it….


No comments:
Post a Comment